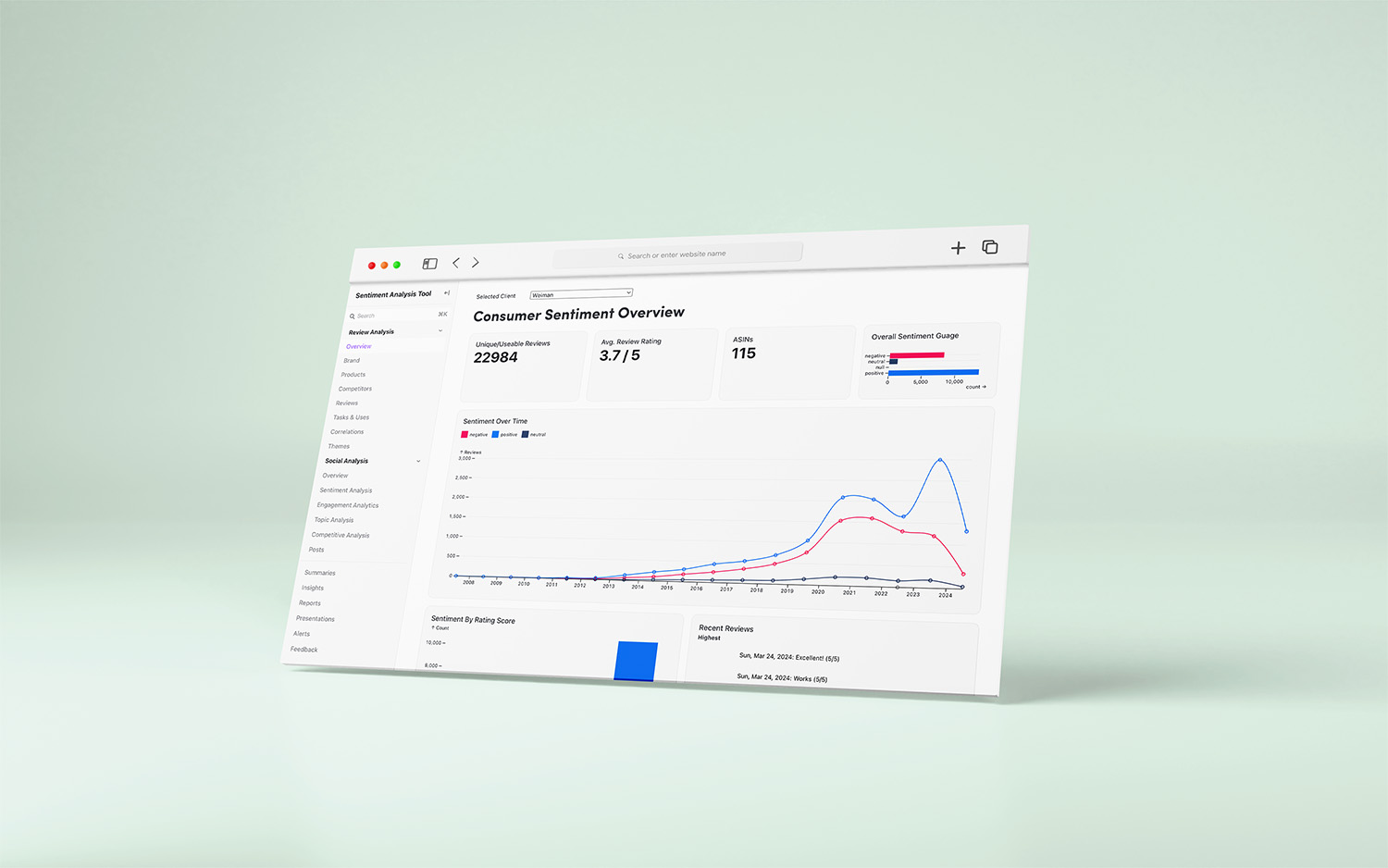
The landscape of data analysis has evolved significantly with the advent of sophisticated scraping tools and Large Language Models (LLMs). By employing advanced scraping technologies, organizations can now meticulously gather vast amounts of review and social media data, extracting rich insights that were previously inaccessible. Once this data is captured, LLMs come into play, utilizing their extensive training on diverse datasets to analyze the information deeply.
These models are adept at discerning sentiment, distinguishing whether the tone of text is positive, negative, or neutral, which is vital in understanding consumer attitudes. Furthermore, aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) allows businesses to pinpoint specific attributes of a product or service that customers mention in their feedback, providing a granular view of client satisfaction. Named Entity Recognition (NER) capabilities of LLMs enable the identification and categorization of key entities within the text, such as brand names, locations, and individuals, facilitating the organization of data for targeted analysis.
Additionally, the LLMs can identify prevailing topics and themes within large text corpora, uncovering underlying patterns that might inform product development, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements. They can also detect specific tasks or uses of products mentioned by consumers, providing actionable insights into how products are being used in real-world scenarios. By leveraging these advanced tools, businesses can transform unstructured data into a structured goldmine of insights, propelling informed decision-making and strategic planning.